Our owner, Noel Boyer, recently did an interview with KY3 news over the upcoming web worms. Below is an excerpt of the article. All rights go to KY3.
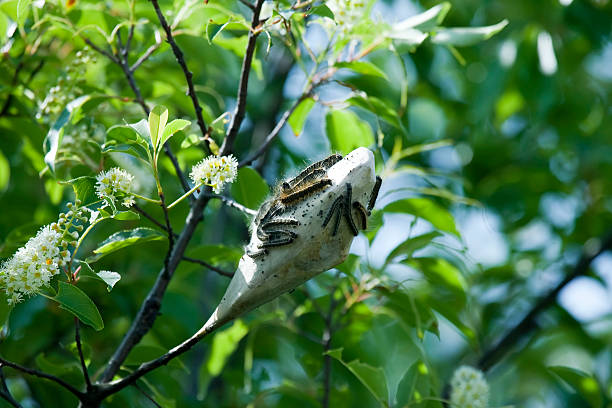

Image source: iStockPhoto
“It will not be long before our trees are laced with web worms.
“I’ve already started to see some web worms when I’m out and about, they are starting to show up in the area,” Kelly McGowan, the Field Horticultural Specialist for the University of Missouri Extension, said.
McGowan said closer to fall, the trees will have more webbing on them. Right now, the caterpillars are small.
“Some years we’ve had it where the trees look like ghosts, they’re so laced with web worm webs,” Noel Boyer, the owner of All About Trees, said.
Before the worms form those ghost-like webs, you may see the caterpillars on the tips of tree branches.
“Once these little caterpillars start to feed on the foliage of the plant, they will expand their webbing and take in more foliage,” McGowan said,
Web worms won’t permanently damage your trees, they are just unsightly.
“If you just can’t stand it, they can be sprayed,” Boyer said.
Use an insecticide specially targeted for web worms. Unless your tree needs it, don’t start pruning.
“It’s just not okay to wound trees over an insect pest that’s not doing any damage to the tree,” Boyer said.
You do not want to burn the branch as it will cause more damage to the tree. McGowan says it is easiest to just wipe the worms off of the tree. Use a gardening glove.
“Basically can just wipe it out of the tree, the webs will fall to the ground,” McGowan said.
If that makes you squeamish, Boyer recommends using a stick to break the webs open. The birds will be able to feed on the caterpillars inside.”
To read the full article at Ky3, click the link below.
Source: https://www.ky3.com/2021/08/05/watch-out-these-worms-your-trees/