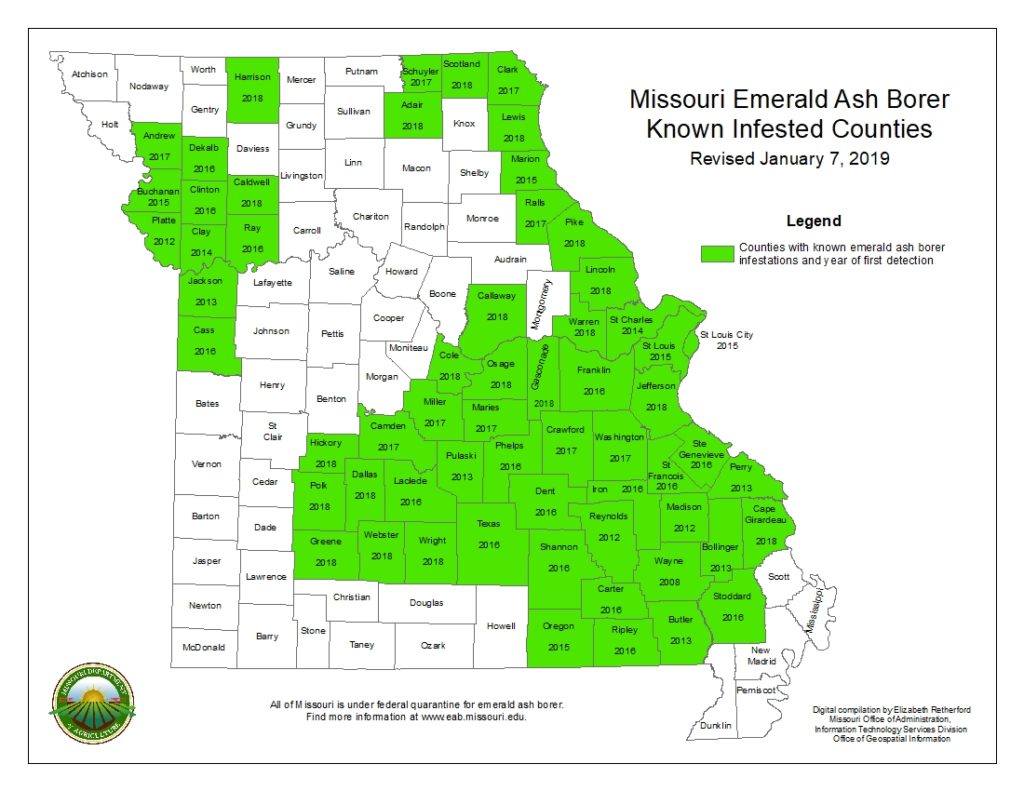
What is the Cause of Dutch Elm Disease?
Dutch elm disease (DED) is caused by an aggressive fungus (Ophiostoma novo-ulmi) that kills elm trees – regardless of their health. It is considered the most costly shade tree disease ever and will remain active in a community as long as there are susceptible trees. The fungus invades the water transporting vessels and produces toxins. To try and defend against the toxins, the tree produces gums and internal growths designed to block the advance of the fungus. The combination of the toxins and the defense mechanisms of the tree inhibits water flow to the crown, which causes wilting and eventual tree death.
How Does Dutch Elm Disease Spread?
Female elm bark beetles lay their eggs beneath the bark of dead and dying elm trees. If the elm is infected with Dutch elm disease the newly hatched beetles will emerge from the tree carrying the deadly fungus on their bodies. The beetles fly to healthy trees and feed on its 2-4 year old branches, thereby spreading the disease.
Besides beetle transmission, Dutch elm disease may also spread through grafted roots. When elms grow in proximity to each other, their roots can come into contact and graft together. This common root system provides the fungus with a pathway to spread through an entire stand of healthy elms very quickly.
What are the Symptoms of DED?
Dutch elm disease symptoms begin to develop 4 – 6 weeks after infection. The first noticeable symptom that results from the fungal occupation of the water-conducting vessels is wilting or “flagging” of one or more branches, usually starting at the branch tip. Leaves on the infected branches turn dull green to yellow, curl, and become dry and brittle. As the infection spreads the wood beneath the bark displays brown discoloration.
What Can I Do if My Tree is Already Infected?
Most infected elms cannot be saved. In rare cases, if the fungus has not moved into the root system, physically cutting out infected portions of the tree, with a process called tracing, can save the elm.
Sanitation is the most important tool for controlling Dutch elm disease on a community-wide basis. It involves the identification and removal of diseased elms. Such practices eliminate beetle breeding sites and reduce the number of disease-carrying beetles.
Root Grafts
Dutch elm disease can pass from infected trees into healthy trees through grafted roots. Macro-infusion of Arbotect does not prevent root graft infections. The only way to reliably prevent root graft transmission of the fungus is to physically sever the common root system.
How Can I Protect my Elm Tree?
The goal when protecting elms from the fungus is to evenly and completely distribute a fungicide chemical through the entire canopy of the tree.
- To protect the tree from beetle-transmitted fungal infection, Arbotect fungicide must be evenly and completely distributed throughout the 2-4 year old branches.
- The only way to get an even distribution is by a tree injection method called macro-infusion. Macro-infusion injects a large volume of solution into the root flares of the tree. This solution is then transported throughout the canopy by the tree, providing a protective fungicide barrier.
- Arbortect fungicide does not protect elms from root graft infection. You need to physically sever the root system from neighboring trees by trenching at least 36″ down.
Source: Rainbow Treecare Scientific Advancements, 2005.
Want to read more about tree diseases and pests? Click here to read our article on Emerald Ash Borer, an equally destructive scrouge to trees.
All About Trees is caring for Springfield’s urban forest, one tree at a time.